Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4), also known as CD152, is a leukocyte differentiation antigen. ReadCrystal has completed the protein expression and structural analysis of CTLA-4 target. Based on these experimental conditions and stock proteins, we reduced the project delivery time to 1-2 months and ensured the successful delivery of the project.
CTLA-4 Protein
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4), also known as CD152, is a transmembrane receptor on T cells, and shares the B7 molecular ligand with CD28. The binding of CTLA-4 to B7 induces T cells to be non-reactive and participate in the negative regulation of immune response. Recombinant CTLA-4 Ig can effectively and specifically inhibit cellular and humoral immune responses in vivo and in vitro, and has significant therapeutic effects on transplant rejection and various autoimmune diseases, with very low side effects, so it is considered a promising new immunosuppressive drug at present.
Mutations in the CTLA-4 gene have been linked to type 1 diabetes, Graves' disease, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, celiac disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, thyroid-associated orbital disease, primary biliary cirrhosis, and other autoimmune diseases. Germ line haploid deficiency of CTLA4 leads to CTLA4 deficiency or CHAI disease (CTLA4 haploid deficiency with autoimmune infiltration), which is a rare genetic disorder of the immune system. This can lead to a disorder of the immune system and can lead to lymphocyte proliferation, autoimmunity, hypogammaglobulinemia, repeated infections, and may slightly increase the risk of lymphoma.
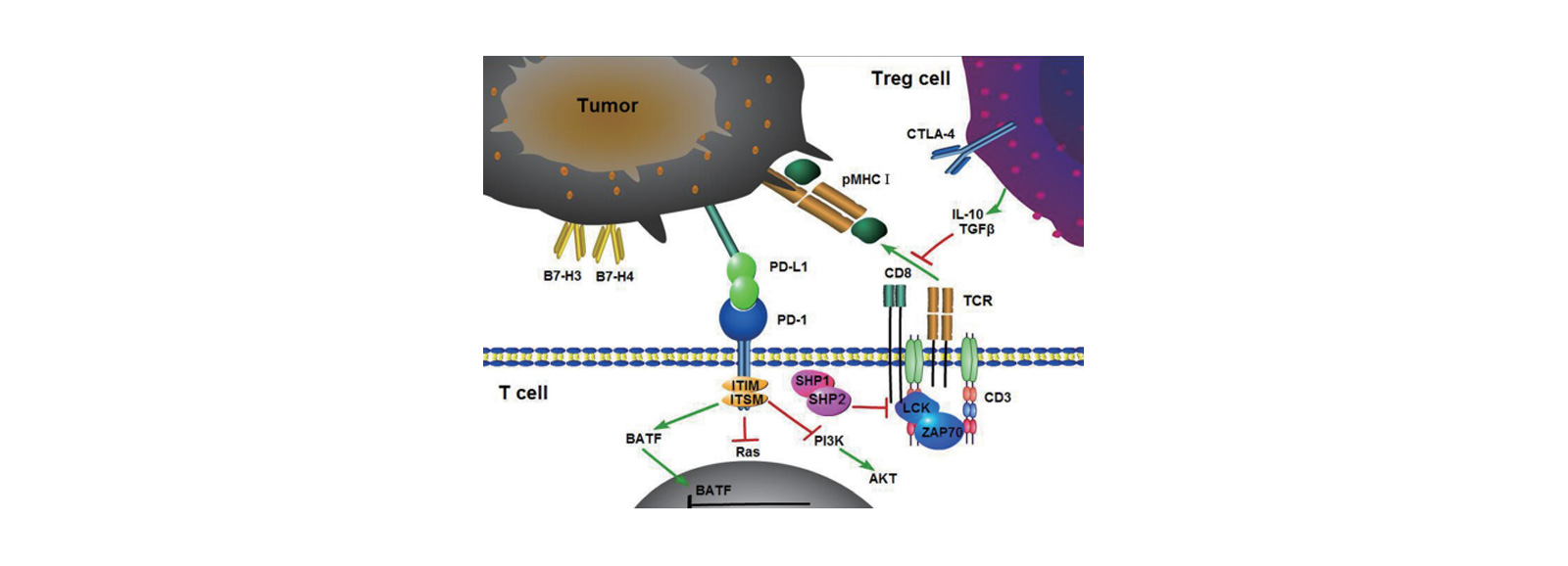
Figure 1. The mechanism of tumor immune escape caused by the imbalance of CTLA-4 and PD-1[1]
Our Capability
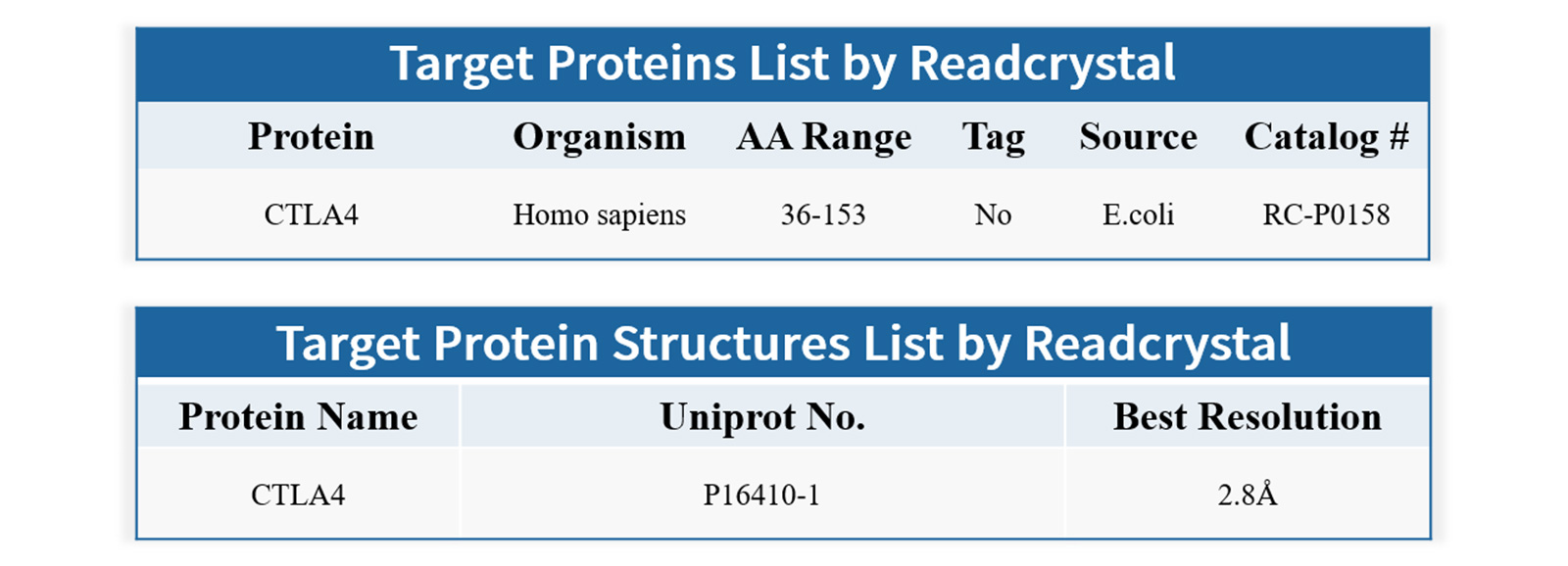
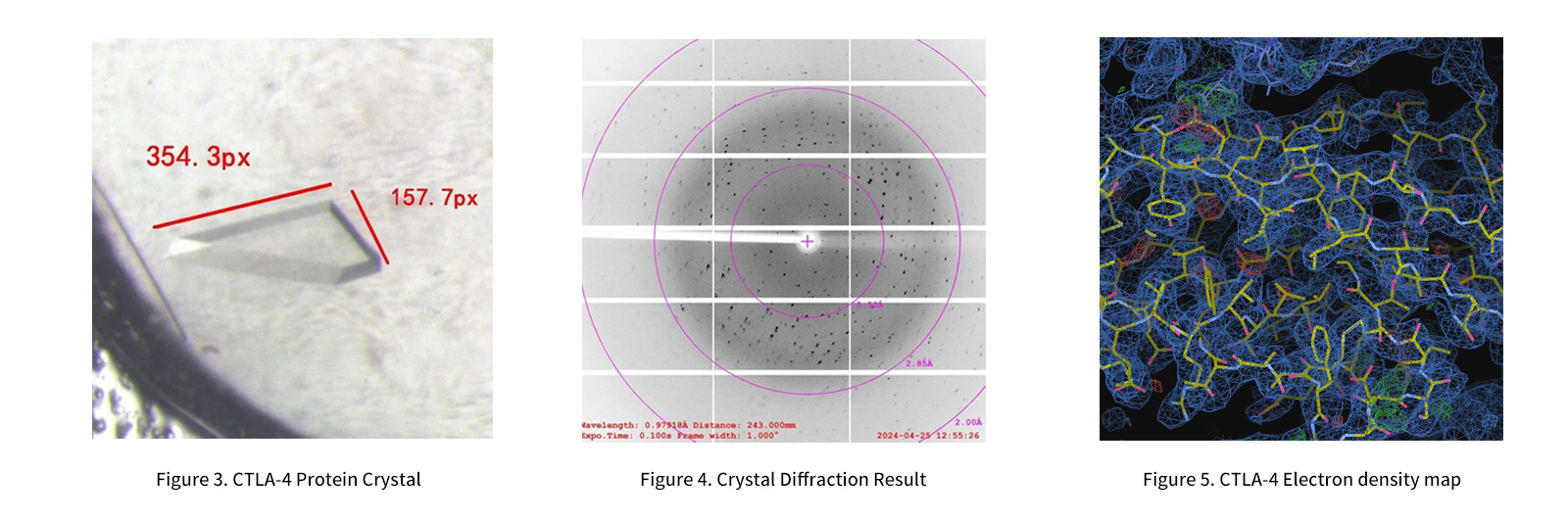
CTLA-4 protein experimental results
Protein Purification Result(Period: in stock/3 weeks)
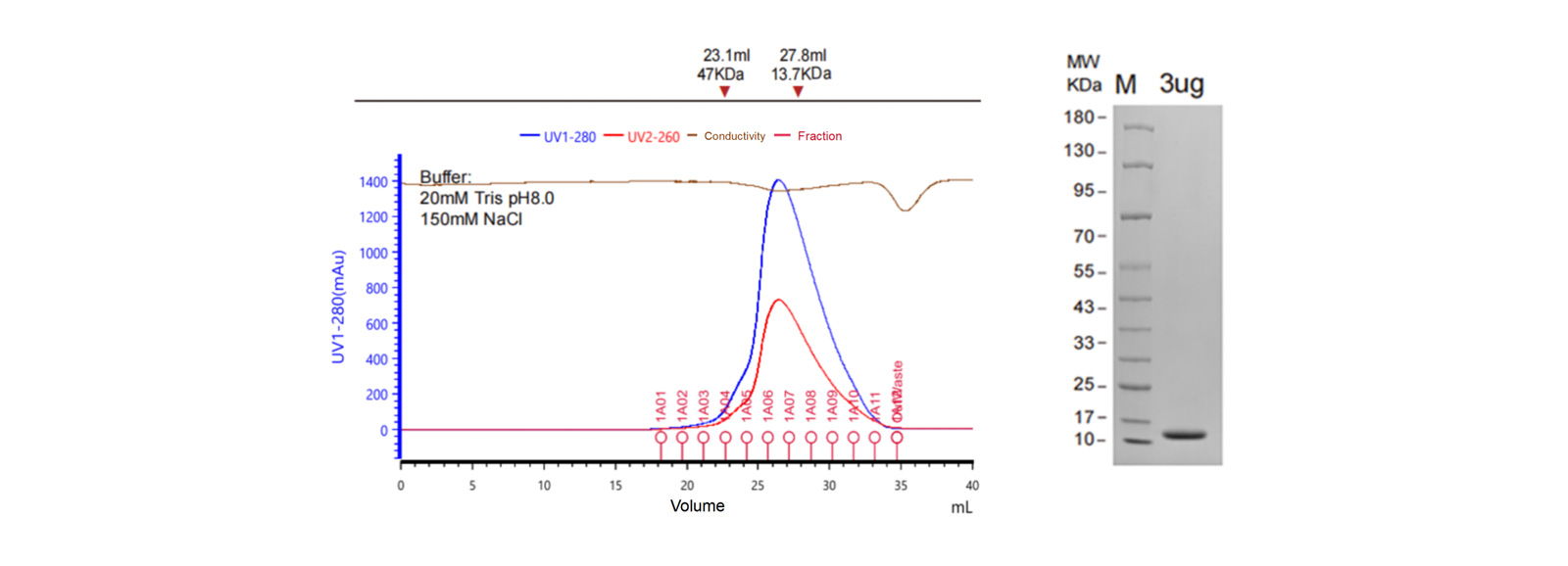
Figure 2. CTLA-4 Protein Purification result
Crystallization and Structural Analysis(Period: 1-2 weeks)