HPK1 protein is an important class of protein kinases. ReadCrystal has completed the protein expression and structural analysis of multiple HPK1 mutation targets. Based on these experimental conditions and the stock of proteins, ReadCrystal has reduced the project delivery time to 1-2 months while ensuring the successful delivery of the project.
HPK1 Protein
Hematopoietic progenitor kinase-1 (HPK1) is a hematopoietic-specific protein serine-threonine kinase, also known as Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 1 (MAP4K1). It is a member of the mammalian Ste20-related protein kinase MAP4K family. The kinases in the MAP4K family have highly similar protein structures and play critical roles in regulating cell survival, migration, apoptosis, and autophagy.
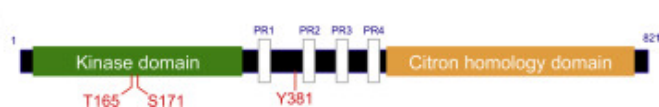
Figure 1. Basic Structure of HPK1
HPK1 is primarily expressed in lymphoid organs/tissues, including bone marrow, lymph nodes, thymus, spleen, placenta, and fetal liver. It is also expressed in all hematopoietic and immune cells, such as hematopoietic progenitor cells, T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. HPK1 kinase is a key negative feedback regulator of TCR signaling, capable of downregulating dendritic cell activation and feedback from T cells, neutrophils, and mast cells to B cells. Inhibiting HPK1 can enhance T-cell activity, thereby boosting anti-tumor immunity.
In T-cells, TCR engagement triggers a series of events near the membrane’s lipid rafts, including the activation of tyrosine kinases Lck and Zap70, and the recruitment of the adaptor protein SLP76 to LAT. Additional signaling proteins associate with SLP76, forming a signaling complex that leads to T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. After TCR activation, HPK1 is recruited to the TCR complex by adaptor proteins such as Gads and Grb2. Lck/Zap70 phosphorylates HPK1 at the Tyr381 site, creating a docking site for SLP76. HPK1 then phosphorylates Ser376 on SLP76 and Thr254 on Gads, activating SLP76. This phosphorylated complex participates in downregulating the ERK signaling pathway, recruiting 14-3-3 proteins, and subsequently dismantling the TCR complex. As a result, TCR signaling is inhibited, leading to a reduction in TCR signaling pathways and T-cell proliferation (Figure 2).
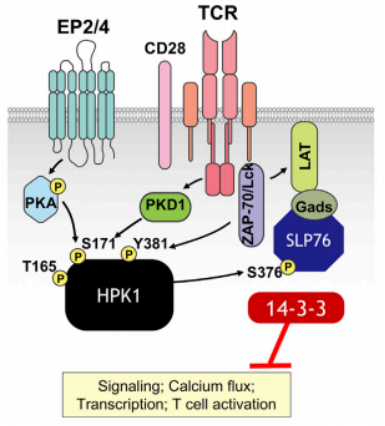
Figure 2. HPK1 Involvement in TCR Signal Negative Regulation
Studies have shown that in autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and psoriatic arthritis, downregulation of HPK1 expression has been detected in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and T cells of patients. Additionally, HPK1 is associated with the development of various malignant tumors. HPK1 is positively correlated with multiple T-cell exhaustion markers (CD3E, TIGIT, PDCD1, CTLA4, HAVCR2, and LAG3). At the same time, HPK1 expression levels are negatively correlated with the survival time of patients with various cancers, such as low-grade glioma, clear cell renal carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, and invasive breast cancer. HPK1 induces dysfunction in tumor-infiltrating T cells, weakening immune responses of T cells, B cells, and dendritic cells, making it a potential target for tumor immunotherapy.
Complete activation of HPK1 kinase activity requires phosphorylation of Thr165 and Ser171 residues in the activation segment (AS). Studies show that Ser171 can be phosphorylated, subsequently activating TCR in a PKD1-dependent manner, while Thr165 appears to be an autophosphorylation site. Activated HPK1 phosphorylates the Ser376 site of SLP76, leading to instability of the TCR signaling complex and hindering downstream T-cell activation and proliferation. The HPK1-Thr165Glu/Ser171Glu mutant (TSEE) can mimic the phosphorylated active state of this kinase, while the HPK1-S171A mutant (SA) can mimic the inactive state. Both mutants are commonly used as structural models to study the mechanism of action of inhibitors.
About ReadCrystal
We has completed structural analysis of HPK1 mutants and co-crystal structures with small molecules. We has accumulated extensive experience in protein expression, purification, and co-crystal structural analysis of inhibitors targeting this protein. We has developed over 100 experimental conditions for these studies. The project delivery time can be as short as one month, ensuring successful project completion.